Wie man PHP-Einstellungen (php.ini) auf cPanel ändert
Geschätzte Zeit: 10 Minuten
Schwierigkeit: Mittel ⭐⭐
Voraussetzungen: Zugriff auf cPanel
📋 Einführung
Die Datei php.ini ist die Hauptkonfigurationsdatei von PHP. Sie steuert wichtige Einstellungen wie:
- 📦 Die maximale Upload-Größe von Dateien
- 🧠 Der Script zugewiesene Speicher
- ⏱️ Die Script-Ausführungszeit
- 🔧 Die aktivierten PHP-Erweiterungen
- 🐛 Die Fehleranzeige
Auf cPanel können Sie diese Einstellungen einfach mit dem MultiPHP INI Editor ändern, ohne die Konfigurationsdateien manuell bearbeiten zu müssen.
🎯 Wann PHP-Einstellungen ändern?
Gängige Situationen
| ❌ Aufgetretenes Problem | ✅ Zu ändernde Einstellung |
|---|---|
| "Die hochgeladene Datei überschreitet die upload_max_filesize" | upload_max_filesize |
| "Erlaubte Speichergröße erschöpft" | memory_limit |
| "Maximale Ausführungszeit überschritten" | max_execution_time |
| "Post Content-Length überschreitet das Limit" | post_max_size |
| Komplexe Formulare werden nicht gespeichert | max_input_vars |
| Timeout bei Importen/Exporten | max_input_time |
| Fehler 500 auf WordPress/WooCommerce-Websites | Mehrere Einstellungen |
📊 Wichtige PHP-Einstellungen
Zusammenfassungstabelle
| Einstellung | Beschreibung | Standardserver | Empfohlen für WordPress | Empfohlen für WooCommerce |
|---|---|---|---|---|
memory_limit | Maximaler Speicher pro Skript | 128M | 256M | 512M |
upload_max_filesize | Maximale Größe einer hochgeladenen Datei | 2M - 64M | 64M | 128M |
post_max_size | Maximale Größe der per POST gesendeten Daten | 8M | 128M | 256M |
max_execution_time | Maximale Ausführungsdauer (Sekunden) | 30 | 300 | 600 |
max_input_time | Maximale Zeit zum Parsen von Eingabedaten (Sekunden) | 60 | 300 | 600 |
max_input_vars | Maximale Anzahl akzeptierter Eingabevariablen (Formularfelder) | 1000 | 3000 | 5000 |
📖 Detaillierte Beschreibung der Einstellungen
🧠 memory_limit
Beschreibung: Maximale Menge an Speicher, die ein PHP-Skript verwenden kann.
memory_limit = 256M
| Art der Website | Empfohlener Wert |
|---|---|
| Einfache Showcase-Website | 128M |
| WordPress-Blog | 256M |
| WordPress + Plugins | 256M - 512M |
| WooCommerce | 512M |
| Schwere PHP-Anwendung | 512M - 1024M |
Zugehöriger Fehler:
Schwerwiegender Fehler: Erlaubte Speichergröße von 134217728 Bytes erschöpft
⚠️ Wichtig:
memory_limitmuss größer oder gleichpost_max_sizesein.
📤 upload_max_filesize
Beschreibung: Maximale Größe einer einzelnen Datei beim Hochladen.
upload_max_filesize = 64M
| Verwendung | Empfohlener Wert |
|---|---|
| Optimierte Webbilder | 16M |
| Hochauflösende Fotos | 32M |
| WordPress-Themes/Plugins | 64M |
| Kurze Videos | 128M |
| Große Dateien | 256M+ |
Zugehöriger Fehler:
Die hochgeladene Datei überschreitet die upload_max_filesize-Direktive in der php.ini
💡 Tipp: Überprüfen Sie auch die WordPress-Limits: Medien → Hinzufügen.
📨 post_max_size
Beschreibung: Maximale Gesamtgröße der über POST gesendeten Daten (beinhaltet hochgeladene Dateien).
post_max_size = 128M
Wichtige Regel:
post_max_size ≥ upload_max_filesize
💡 Tipp: Setzen Sie
post_max_sizeleicht überupload_max_filesize, um Metadaten zu berücksichtigen.
Beispiel:
upload_max_filesize = 64Mpost_max_size = 68Moder128M
Zugehöriger Fehler:
Warnung: POST Content-Length von X Bytes überschreitet das Limit von Y Bytes
⏱️ max_execution_time
Beschreibung: Maximale Dauer (in Sekunden), während der ein Skript ausgeführt werden kann.
max_execution_time = 300
| Vorgang | Empfohlener Wert |
|---|---|
| Normales Browsen | 30 (Standard) |
| WordPress-Import/Export | 300 |
| Berichterstellung | 300 - 600 |
| Website-Migration | 600 - 900 |
| Automatische Backups | 600 |
Zugehöriger Fehler:
Schwerwiegender Fehler: Maximale Ausführungszeit von 30 Sekunden überschritten
⚠️ Achtung: Auf Shared Hosting kann dieser Wert begrenzt sein (oft auf 90-120 Sekunden).
⏳ max_input_time
Beschreibung: Maximale Dauer (in Sekunden) zum Parsen von Eingabedaten (POST, GET, Uploads).
max_input_time = 300
| Situation | Empfohlener Wert |
|---|---|
| Einfache Formulare | 60 (Standard) |
| Hochladen großer Dateien | 300 |
| CSV/XML-Import | 300 - 600 |
| Langsame Verbindung | 600 |
💡
-1= keine Begrenzung (nicht empfohlen für die Produktion).
🔢 max_input_vars
Beschreibung: Maximale Anzahl akzeptierter Eingabevariablen (Formularfelder).
max_input_vars = 3000
| Art des Inhalts | Empfohlener Wert |
|---|---|
| Einfache Website | 1000 (Standard) |
| WordPress mit komplexen Menüs | 3000 |
| WooCommerce mit Attributen | 5000 |
| Page Builder (Elementor, Divi) | 5000 - 10000 |
Symptome bei zu niedriger Einstellung:
- WordPress-Menüs, die nicht vollständig gespeichert werden
- Theme-Optionen, die verschwinden
- Nicht gespeicherte WooCommerce-Varianten
🐛 display_errors
Beschreibung: Zeigt PHP-Fehler direkt auf der Seite an.
display_errors = Off # Production (recommended)
display_errors = On # Development only
⚠️ Security: Always disabled in production! Errors can reveal sensitive information.
📝 error_reporting
Description: Level of detail of errors to report.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
E_ALL | All errors |
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE | Errors except notices |
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_DEPRECATED | Without notices or deprecations |
0 | No errors |
Recommended for production:
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
📁 error_log
Description: Path to the file where errors are logged.
error_log = /home/user/logs/php_errors.log
💡 Useful for debugging without displaying errors to visitors.
🔒 allow_url_fopen
Description: Allows opening remote files via URL.
allow_url_fopen = On # Often required for WordPress
Used by:
- WordPress updates
- Retrieval of RSS feeds
- External APIs
🔐 allow_url_include
Description: Allows inclusion of remote files via include/require.
allow_url_include = Off # Always disabled (security)
⚠️ Security: Never enable! Major risk of code injection.
⚙️ Method 1: MultiPHP INI Editor (Basic Mode)
The basic mode offers a simple interface with pre-configured fields.
Step 1: Access MultiPHP INI Editor
- Log in to cPanel
- In the Software section, click on MultiPHP INI Editor
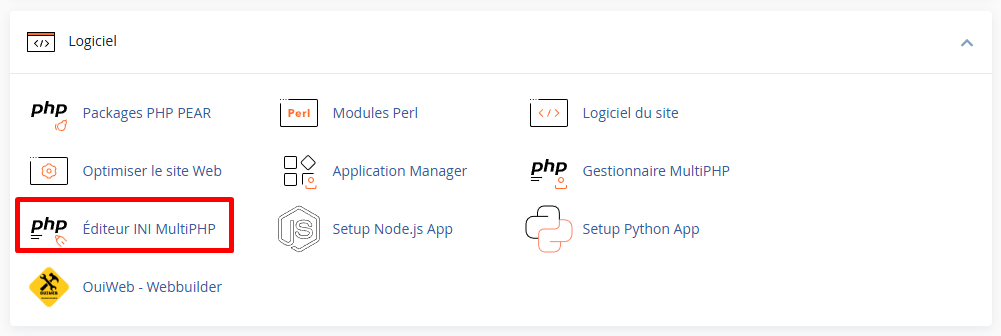
Step 2: Select the location
- Stay on the Basic Mode tab
- In the dropdown menu "Select a location", choose:
- Personal directory (
home): Applies to all domains - Domain document root: Applies only to this domain
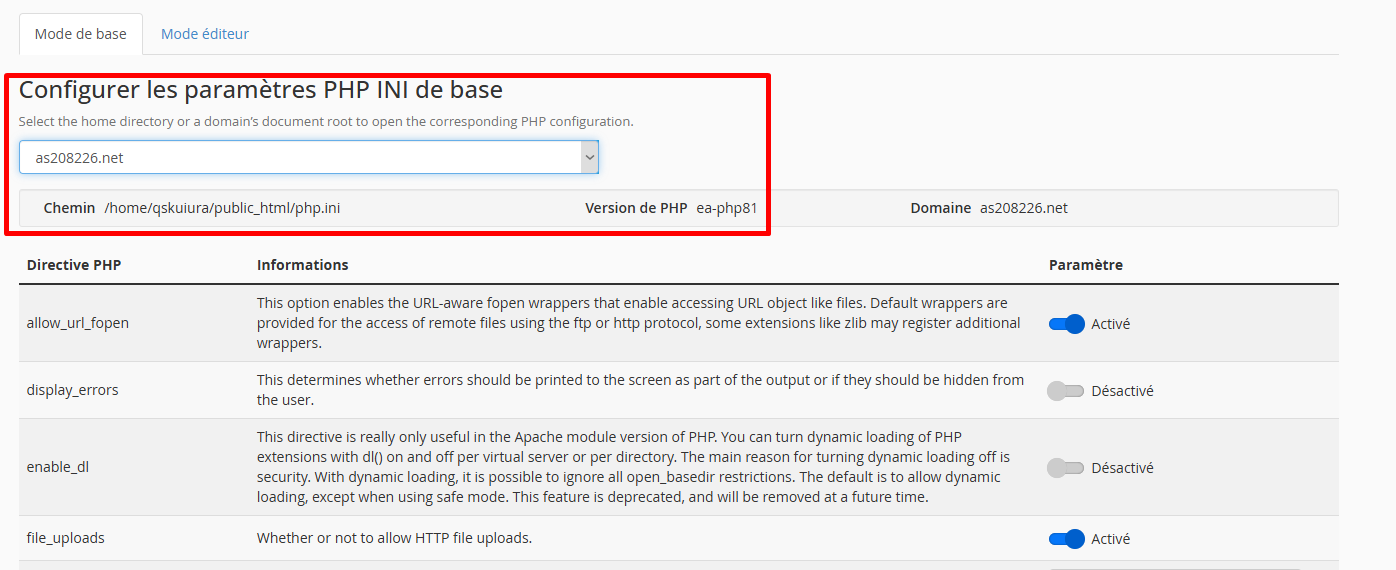
- Personal directory (
💡 Tip: To modify a single site, select its document root (e.g.,
public_html/mysite.com).
Step 3: Modify the settings
After selecting the location, a list of PHP directives appears:
| Directive | Field to modify |
|---|---|
memory_limit | Enter 256M |
upload_max_filesize | Enter 64M |
post_max_size | Enter 128M |
max_execution_time | Enter 300 |
max_input_time | Enter 300 |
max_input_vars | Enter 3000 |
Step 4: Apply the changes
- Click on the Apply button
- A confirmation message appears:
✅ PHP settings have been successfully updated.
💡 Changes are immediate. No restart required.
🔧 Method 2: MultiPHP INI Editor (Editor Mode)
The editor mode allows adding custom directives not available in basic mode.
Step 1: Switch to Editor Mode
- In MultiPHP INI Editor, click on the Editor Mode tab
- Select the location (domain or personal directory)
Step 2: Add directives
A text area displays the current content of the php.ini file. You can add lines:
; === CUSTOM CONFIGURATION ===
; Memory and limits
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
; Execution time
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
; Input variables
max_input_vars = 5000
; Error handling (production)
display_errors = Off
log_errors = On
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; Sessions
session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440
; Timezone
date.timezone = Europe/Paris
Step 3: Save
- Click on Save
- Verify that the changes are applied (see Verification section)
📝 Method 3: .htaccess File
If MultiPHP INI Editor is not available, you can modify settings via .htaccess.
Add directives
Open the .htaccess file at the root of your site and add:
# === PHP CONFIGURATION ===
# Memory
php_value memory_limit 256M
# Upload
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
php_value post_max_size 128M
# Execution time
php_value max_execution_time 300
php_value max_input_time 300
# Variables
php_value max_input_vars 3000
# Errors (production)
php_flag display_errors Off
php_flag log_errors On
⚠️ Important: This method only works with the Apache handler (mod_php or suPHP). It does not work with PHP-FPM or CGI.
📄 Method 4: Custom php.ini File
You can create a php.ini file in your site's folder.
Create the file
- Using the File Manager in cPanel, go to
public_html - Create a new file named
php.ini - Add the content:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
💡 On some servers, the file must be named
.user.iniinstead ofphp.ini.
📄 Method 5: .user.ini File (PHP-FPM)
For servers using PHP-FPM, create a .user.ini file:
Create the file
- In
public_html, create.user.ini - Add:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
⚠️ Changes via
.user.inimay take 5 minutes to apply (PHP-FPM cache).
✅ Verify Changes
Method 1: Via WordPress
- Go to Tools → Site Health → Info
- Expand the Server section
- Überprüfen Sie die Werte:
- PHP-Speicherlimit
- Maximale Upload-Größe
- Maximale Ausführungszeit
- Maximale Eingabevariablen
Methode 2: Über phpinfo()
- Erstellen Sie eine Datei
info.phpinpublic_html:
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
- Gehen Sie zu
https://your-website.com/info.php - Suchen Sie nach geänderten Einstellungen (Strg+F)
- Löschen Sie die Datei nach der Überprüfung (Sicherheit)
Methode 3: Über WordPress (Medien)
- Gehen Sie zu Medien → Hinzufügen
- Die maximale Upload-Größe wird angezeigt:
Maximale Upload-Größe: 64 MB
🎯 Empfohlene Konfigurationen nach Website-Typ
Statische Website / Einfacher Blog
memory_limit = 128M
upload_max_filesize = 32M
post_max_size = 64M
max_execution_time = 120
max_input_time = 120
max_input_vars = 1000
Standard WordPress
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
WordPress + Page Builder (Elementor, Divi, WPBakery)
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 10000
WooCommerce / E-Commerce
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 5000
PrestaShop
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 20000
Benutzerdefinierte PHP-Anwendung / API
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
allow_url_fopen = On
🔧 Fehlerbehebung
Einstellungen werden nicht übernommen
| ❌ Mögliche Ursache | ✅ Lösung |
|---|---|
| Aktiver PHP-Cache | Warten Sie 5 Minuten oder leeren Sie den Cache |
| Falscher Standort ausgewählt | Überprüfen Sie, ob Sie die richtige Domain ausgewählt haben |
| Priorisierter .htaccess-Datei | Entfernen Sie die PHP-Direktiven aus der .htaccess-Datei |
| Inkompatibler PHP-Handler | Verwenden Sie MultiPHP INI Editor anstelle von .htaccess |
| Serverlimit | Kontaktieren Sie den Hosting-Anbieter (einige Werte sind begrenzt) |
Fehler 500 nach Änderung
- Über FTP/Dateimanager:
- Benennen Sie
.htaccessin.htaccess.bakum - Oder entfernen Sie hinzugefügte
php_valueZeilen
- Benennen Sie
- Über MultiPHP INI Editor:
- Gehen Sie zurück zu den Standardwerten
- Ändern Sie eine Direktive nach der anderen, um das Problem zu identifizieren
"php_value not allowed here"
Dieser Fehler bedeutet, dass Ihr Server PHP-FPM oder CGI verwendet:
.htaccess: php_value not allowed here
Lösung: Verwenden Sie MultiPHP INI Editor oder erstellen Sie eine Datei .user.ini.
Die WordPress-Upload-Größe ändert sich nicht
Überprüfen Sie diese Elemente in der Reihenfolge:
- ✅
upload_max_filesizewurde erfolgreich geändert - ✅
post_max_size≥upload_max_filesize - ✅
memory_limit≥post_max_size - ✅ Kein WordPress-Plugin begrenzt den Upload
- ✅ Das Theme setzt keine Grenze
Prioritätsreihenfolge der Dateien:
1. Server php.ini (höchste Priorität)
2. MultiPHP INI Editor
3. .user.ini oder lokale php.ini
4. .htaccess
5. wp-config.php (WordPress)
6. functions.php (Theme)
max_input_vars wird ignoriert
Einige Hosting-Anbieter begrenzen diesen Wert. Lösungen:
- Kontaktieren Sie den Support, um das Limit zu erhöhen
- Wechseln Sie zu einem höheren Tarif
- Optimieren Sie Ihre WordPress-Menüs (weniger Elemente)
📋 Vollständige Liste nützlicher PHP-Direktiven
Speicher und Ressourcen
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
memory_limit | Maximaler Speicher pro Skript | 256M |
max_execution_time | Maximale Ausführungszeit | 300 |
max_input_time | Maximale Eingabezeit | 300 |
max_input_vars | Maximale Anzahl von Variablen | 3000 |
max_input_nesting_level | Maximale Verschachtelungstiefe von Arrays | 64 |
Dateiuploads
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
upload_max_filesize | Maximale Dateigröße | 64M |
post_max_size | Maximale POST-Daten-Größe | 128M |
max_file_uploads | Maximale Anzahl gleichzeitiger Dateiuploads | 20 |
file_uploads | Dateiuploads aktivieren | On |
Fehlerbehandlung
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
display_errors | Fehler anzeigen | Off |
log_errors | Fehler protokollieren | On |
error_reporting | Fehlerlevel | E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE |
error_log | Logdatei | /home/user/logs/error.log |
Sitzungen
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
session.gc_maxlifetime | Lebensdauer der Sitzung (Sekunden) | 1440 |
session.cookie_lifetime | Lebensdauer des Session-Cookies | 0 |
session.save_path | Pfad zum Speichern von Sitzungen | /tmp |
Sicherheit
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
allow_url_fopen | URLs als Dateien öffnen | On |
allow_url_include | Remote-Dateien einbinden | Off |
expose_php | PHP-Version offenlegen | Off |
disable_functions | Deaktivierte Funktionen | exec,shell_exec |
Verschiedenes
| Direktive | Beschreibung | Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
date.timezone | Zeitzone | Europe/Paris |
default_charset | Standardzeichensatz | UTF-8 |
short_open_tag | Short tags <? | Off |
output_buffering | Output buffering | 4096 |
📝 Summary
MODIFY PHP SETTINGS:
METHOD 1 - MultiPHP INI Editor (Recommended):
1. cPanel → Software → MultiPHP INI Editor
2. Select the domain
3. Modify the values
4. Click on Apply
METHOD 2 - Editor Mode:
1. Tab "Editor Mode"
2. Add directives manually
3. Click on Save
METHOD 3 - .htaccess (Apache only):
php_value memory_limit 256M
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
METHOD 4 - .user.ini (PHP-FPM):
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
RECOMMENDED VALUES FOR WORDPRESS:
├── memory_limit = 256M
├── upload_max_filesize = 64M
├── post_max_size = 128M
├── max_execution_time = 300
├── max_input_time = 300
└── max_input_vars = 3000
IMPORTANT RULE:
memory_limit ≥ post_max_size ≥ upload_max_filesize
VERIFICATION:
├── WordPress: Tools → Site Health → Info → Server
├── phpinfo(): Create info.php with <?php phpinfo(); ?>
└── Media: Check the max upload size
