How to modify PHP settings (php.ini) on cPanel
Estimated time: 10 minutes
Difficulty: Intermediate ⭐⭐
Prerequisites: Access to cPanel
📋 Introduction
The php.ini file is the main PHP configuration file. It controls essential settings such as:
- 📦 The maximum file upload size
- 🧠 The memory allocated to scripts
- ⏱️ The script execution time
- 🔧 The enabled PHP extensions
- 🐛 The display of errors
On cPanel, you can easily modify these settings using the MultiPHP INI Editor, without having to manually edit configuration files.
🎯 When to Modify PHP Settings?
Common Situations
| ❌ Issue Encountered | ✅ Setting to Modify |
|---|---|
| "The uploaded file exceeds the upload_max_filesize" | upload_max_filesize |
| "Allowed memory size exhausted" | memory_limit |
| "Maximum execution time exceeded" | max_execution_time |
| "Post Content-Length exceeds the limit" | post_max_size |
| Complex forms not saving | max_input_vars |
| Timeout during imports/exports | max_input_time |
| 500 errors on WordPress/WooCommerce sites | Multiple settings |
📊 Essential PHP Settings
Summary Table
| Setting | Description | Default Server | Recommended for WordPress | Recommended for WooCommerce |
|---|---|---|---|---|
memory_limit | Max memory per script | 128M | 256M | 512M |
upload_max_filesize | Max size of uploaded file | 2M - 64M | 64M | 128M |
post_max_size | Max size of POST data | 8M | 128M | 256M |
max_execution_time | Max execution time (sec) | 30 | 300 | 600 |
max_input_time | Max input data read time (sec) | 60 | 300 | 600 |
max_input_vars | Max number of input variables | 1000 | 3000 | 5000 |
📖 Detailed Description of Settings
🧠 memory_limit
Description: Maximum amount of memory a PHP script can use.
memory_limit = 256M
| Site Type | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Simple showcase site | 128M |
| WordPress blog | 256M |
| WordPress + plugins | 256M - 512M |
| WooCommerce | 512M |
| Heavy PHP application | 512M - 1024M |
Associated Error:
Fatal error: Allowed memory size of 134217728 bytes exhausted
⚠️ Important:
memory_limitmust be greater than or equal topost_max_size.
📤 upload_max_filesize
Description: Maximum size of an individual file during upload.
upload_max_filesize = 64M
| Usage | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Optimized web images | 16M |
| High-resolution photos | 32M |
| WordPress themes/plugins | 64M |
| Short videos | 128M |
| Large files | 256M+ |
Associated Error:
The uploaded file exceeds the upload_max_filesize directive in php.ini
💡 Tip: Also check WordPress limits: Media → Add.
📨 post_max_size
Description: Maximum total size of data sent via POST (includes uploaded files).
post_max_size = 128M
Important Rule:
post_max_size ≥ upload_max_filesize
💡 Tip: Set
post_max_sizeslightly higher thanupload_max_filesizeto account for metadata.
Example:
upload_max_filesize = 64Mpost_max_size = 68Mor128M
Associated Error:
Warning: POST Content-Length of X bytes exceeds the limit of Y bytes
⏱️ max_execution_time
Description: Maximum duration (in seconds) a script can run for.
max_execution_time = 300
| Operation | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Normal browsing | 30 (default) |
| WordPress import/export | 300 |
| Report generation | 300 - 600 |
| Site migration | 600 - 900 |
| Automatic backups | 600 |
Associated Error:
Fatal error: Maximum execution time of 30 seconds exceeded
⚠️ Attention: On shared hosting, this value may be capped (often at 90-120 seconds).
⏳ max_input_time
Description: Maximum duration (in seconds) to parse input data (POST, GET, uploads).
max_input_time = 300
| Situation | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Simple forms | 60 (default) |
| Uploading large files | 300 |
| CSV/XML imports | 300 - 600 |
| Slow connection | 600 |
💡
-1= no limit (not recommended for production).
🔢 max_input_vars
Description: Maximum number of accepted input variables (form fields).
max_input_vars = 3000
| Content Type | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Simple site | 1000 (default) |
| WordPress with complex menus | 3000 |
| WooCommerce with attributes | 5000 |
| Page builders (Elementor, Divi) | 5000 - 10000 |
Symptoms if too low:
- WordPress menus not saving completely
- Theme options disappearing
- Unsaved WooCommerce variations
🐛 display_errors
Description: Displays PHP errors directly on the page.
display_errors = Off # Production (recommended)
display_errors = On # Development only
⚠️ Security: Always disabled in production! Errors can reveal sensitive information.
📝 error_reporting
Description: Level of detail of errors to report.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
E_ALL | All errors |
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE | Errors except notices |
E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_DEPRECATED | No notices or deprecations |
0 | No errors |
Recommended for production:
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
📁 error_log
Description: Path to the file where errors are logged.
error_log = /home/user/logs/php_errors.log
💡 Useful for debugging without displaying errors to visitors.
🔒 allow_url_fopen
Description: Allows opening remote files via URL.
allow_url_fopen = On # Often required for WordPress
Used by:
- WordPress updates
- Retrieval of RSS feeds
- External APIs
🔐 allow_url_include
Description: Allows inclusion of remote files via include/require.
allow_url_include = Off # Always disabled (security)
⚠️ Security: Never enable! Major risk of code injection.
⚙️ Method 1: MultiPHP INI Editor (Basic Mode)
The basic mode offers a simple interface with pre-configured fields.
Step 1: Access MultiPHP INI Editor
- Log in to cPanel
- In the Software section, click on MultiPHP INI Editor
Step 2: Select the Location
- Stay on the Basic Mode tab
- In the dropdown menu "Select a location", choose:
- Personal directory (
home): Applies to all domains - Domain's Document root: Applies only to this domain
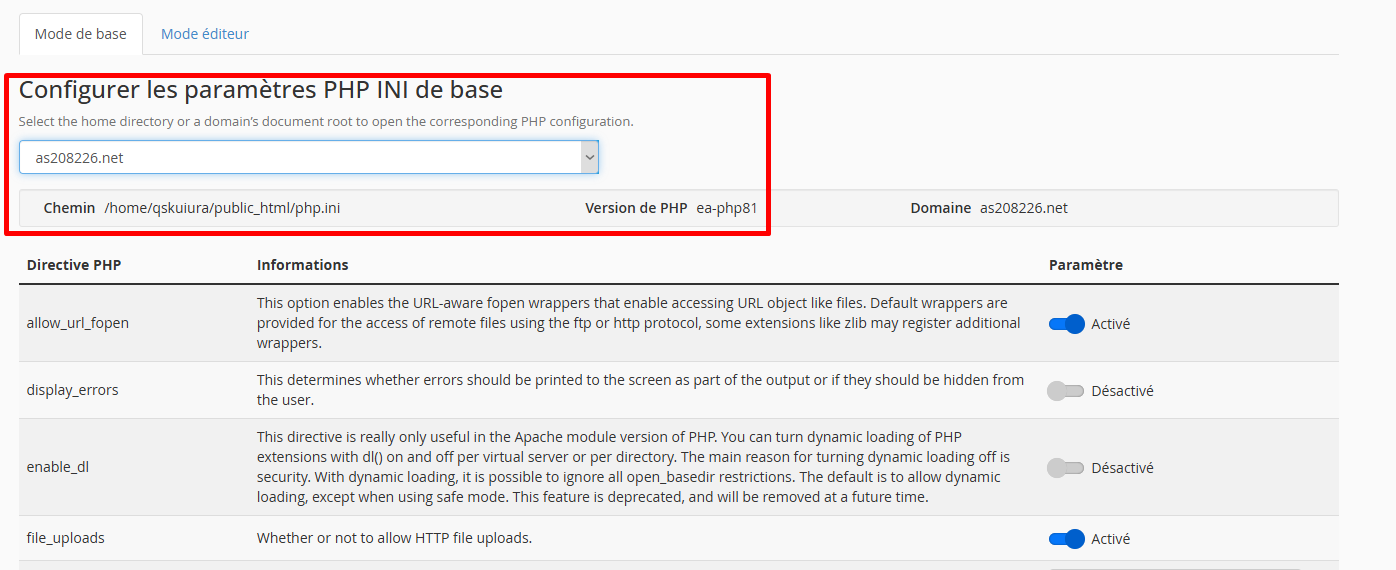
- Personal directory (
💡 Tip: To modify a single site, select its document root (e.g.,
public_html/mysite.com).
Step 3: Modify the Settings
After selecting the location, a list of PHP directives appears:
| Directive | Field to modify |
|---|---|
memory_limit | Enter 256M |
upload_max_filesize | Enter 64M |
post_max_size | Enter 128M |
max_execution_time | Enter 300 |
max_input_time | Enter 300 |
max_input_vars | Enter 3000 |
Step 4: Apply the Changes
- Click on the Apply button
- A confirmation message appears:
✅ PHP settings have been successfully updated.
💡 Changes are immediate. No restart required.
🔧 Method 2: MultiPHP INI Editor (Editor Mode)
The editor mode allows adding custom directives not available in basic mode.
Step 1: Switch to Editor Mode
- In MultiPHP INI Editor, click on the Editor Mode tab
- Select the location (domain or personal directory)
Step 2: Add Directives
A text area displays the current content of the php.ini file. You can add lines:
; === CUSTOM CONFIGURATION ===
; Memory and limits
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
; Execution time
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
; Input variables
max_input_vars = 5000
; Error handling (production)
display_errors = Off
log_errors = On
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; Sessions
session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440
; Timezone
date.timezone = Europe/Paris
Step 3: Save
- Click Save
- Verify that the changes are applied (see Verification section)
📝 Method 3: .htaccess File
If MultiPHP INI Editor is not available, you can modify settings via .htaccess.
Add Directives
Open the .htaccess file at the root of your site and add:
# === PHP CONFIGURATION ===
# Memory
php_value memory_limit 256M
# Upload
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
php_value post_max_size 128M
# Execution time
php_value max_execution_time 300
php_value max_input_time 300
# Variables
php_value max_input_vars 3000
# Errors (production)
php_flag display_errors Off
php_flag log_errors On
⚠️ Important: This method only works with the Apache handler (mod_php or suPHP). It does not work with PHP-FPM or CGI.
📄 Method 4: Custom php.ini File
You can create a php.ini file in your site's directory.
Create the File
- Using the File Manager in cPanel, go to
public_html - Create a new file named
php.ini - Add the content:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
💡 On some servers, the file must be named
.user.iniinstead ofphp.ini.
📄 Method 5: .user.ini File (PHP-FPM)
For servers using PHP-FPM, create a .user.ini file:
Create the File
- In
public_html, create.user.ini - Add:
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
⚠️ Changes via
.user.inimay take 5 minutes to apply (PHP-FPM cache).
✅ Verify Changes
Method 1: Via WordPress
- Go to Tools → Site Health → Info
- Scroll down to the Server section
- Check the values:
- PHP memory limit
- Maximum upload size
- Max execution time
- Max input variables
Method 2: Via phpinfo()
- Create a file
info.phpinpublic_html:
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
- Go to
https://your-site.com/info.php - Look for the modified settings (Ctrl+F)
- Delete the file after checking (security)
Method 3: Via WordPress (Media)
- Go to Media → Add
- The maximum upload size is displayed:
Maximum upload size: 64 MB
🎯 Recommended Configurations by Site Type
Showcase Site / Simple Blog
memory_limit = 128M
upload_max_filesize = 32M
post_max_size = 64M
max_execution_time = 120
max_input_time = 120
max_input_vars = 1000
Standard WordPress
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
WordPress + Page Builder (Elementor, Divi, WPBakery)
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 10000
WooCommerce / E-commerce
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 5000
PrestaShop
memory_limit = 512M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
post_max_size = 128M
max_execution_time = 600
max_input_time = 600
max_input_vars = 20000
Custom PHP Application / API
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
post_max_size = 256M
max_execution_time = 300
max_input_time = 300
max_input_vars = 3000
allow_url_fopen = On
🔧 Troubleshooting
Changes Not Taking Effect
| ❌ Possible Cause | ✅ Solution |
|---|---|
| Active PHP cache | Wait 5 minutes or clear the cache |
| Incorrect selected location | Ensure you have selected the correct domain |
| Priority .htaccess file | Remove PHP directives from .htaccess |
| Incompatible PHP handler | Use MultiPHP INI Editor instead of .htaccess |
| Server limit | Contact the host (some values are capped) |
Error 500 After Modification
- Using FTP/File Manager:
- Rename
.htaccessto.htaccess.bak - Or remove added
php_valuelines
- Rename
- Using MultiPHP INI Editor:
- Revert to default values
- Modify one directive at a time to identify the issue
"php_value not allowed here"
This error means your server uses PHP-FPM or CGI:
.htaccess: php_value not allowed here
Solution: Use MultiPHP INI Editor or create a .user.ini file.
WordPress Upload Size Not Changing
Check these elements in order:
- ✅
upload_max_filesizeis properly modified - ✅
post_max_size≥upload_max_filesize - ✅
memory_limit≥post_max_size - ✅ No WordPress plugin limits the upload
- ✅ The theme does not set a limit
File Priority Order:
1. Server php.ini (highest priority)
2. MultiPHP INI Editor
3. .user.ini or local php.ini
4. .htaccess
5. wp-config.php (WordPress)
6. functions.php (theme)
max_input_vars Ignored
Some hosts cap this value. Solutions:
- Contact support to increase the limit
- Upgrade to a higher plan
- Optimize your WordPress menus (fewer items)
📋 Complete List of Useful PHP Directives
Memory and Resources
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
memory_limit | Max memory per script | 256M |
max_execution_time | Max execution time | 300 |
max_input_time | Max input data read time | 300 |
max_input_vars | Max number of variables | 3000 |
max_input_nesting_level | Max array nesting depth | 64 |
File Uploads
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
upload_max_filesize | Max file size | 64M |
post_max_size | Max POST data size | 128M |
max_file_uploads | Max simultaneous uploads | 20 |
file_uploads | Allow uploads | On |
Error Handling
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
display_errors | Show errors | Off |
log_errors | Log errors | On |
error_reporting | Error reporting level | E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE |
error_log | Log file | /home/user/logs/error.log |
Sessions
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
session.gc_maxlifetime | Session max lifetime (sec) | 1440 |
session.cookie_lifetime | Session cookie lifetime | 0 |
session.save_path | Session storage path | /tmp |
Security
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
allow_url_fopen | Open URL as file | On |
allow_url_include | Include remote files | Off |
expose_php | Reveal PHP version | Off |
disable_functions | Disabled functions | exec,shell_exec |
Miscellaneous
| Directive | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
date.timezone | Timezone | Europe/Paris |
default_charset | Default encoding | UTF-8 |
short_open_tag | Short tags <? | Off |
output_buffering | Output buffering | 4096 |
📝 Summary
MODIFY PHP SETTINGS:
METHOD 1 - MultiPHP INI Editor (Recommended):
1. cPanel → Software → MultiPHP INI Editor
2. Select the domain
3. Modify the values
4. Click Apply
METHOD 2 - Editor Mode:
1. "Editor Mode" tab
2. Add directives manually
3. Click Save
METHOD 3 - .htaccess (Apache only):
php_value memory_limit 256M
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
METHOD 4 - .user.ini (PHP-FPM):
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
RECOMMENDED WORDPRESS VALUES:
├── memory_limit = 256M
├── upload_max_filesize = 64M
├── post_max_size = 128M
├── max_execution_time = 300
├── max_input_time = 300
└── max_input_vars = 3000
IMPORTANT RULE:
memory_limit ≥ post_max_size ≥ upload_max_filesize
VERIFICATION:
├── WordPress: Tools → Site Health → Info → Server
├── phpinfo(): Create info.php with <?php phpinfo(); ?>
└── Media: Check max upload size
